Reducing energy demand in dwellings is an important component of meeting carbon reduction targets. The drivers of such demand reduction are linked to occupant practices, varying greatly between people and locations.
ECCD research has shown that occupants’ thermal preferences can adapt to prolonged high indoor air temperatures, raising their expectations. It also has identified that in the absence of communal heating charges, proportion of UK households are unlikely to be able to afford to heat their homes to the recommended healthy standards.
A human – centric approach working in collaboration with local authorities and residents is required to achieve energy savings without compromising people’s health and well-being.


Updates:
Dr Obaid Malik 2026 
Researcher in Energy, Energy Efficiency and Energy Analytics
UKRI Press Release featuring ECCD research – LATENT 2025 
LATENT project featured in a new UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) press release
Assessment of potential for rooftop solar PV in Hampshire and Sussex 2025 
Rooftop solar means greater generation of renewable energy, closer to where it is used. However, understanding the possible scale of rooftop solar requires mapping the potential, building by building.
ECCD organise Sustainability Strategic Plan: 2024 update 2024 
ECCD organise and host the Sustainability Implementation Group (SIG) update event for the Sustainability Strategic Plan
ECCD exhibit at the Southampton Science and Engineering Festival (SOTSEF) 2024 2024 
The Energy and Climate Change Division exhibited at The Science and Engineering Day held across Highfield Campus and Boldrewood Innovation Campus on Saturday 16th March 2024.
Guidelight – UK Power Networks, electricity distribution 2024 
Low-income and vulnerable consumers receive grant funded LCTs through local authority retrofit schemes, but without supporting households to switch tariffs or using digital optimisation tools, retrofit schemes risk creating a socio-technical performance gap that this project will evidence and address through a range of capability-based interventions that are tailored to those in vulnerable circumstances.
Energy and Sustainability MSc student wins best paper award at the People and Buildings Conference for Masters Students 2023 
Yu Gao, an Energy and Sustainability MSc student supervised by Prof. Patrick James wins the best paper award at the 2023 People and Buildings Conference for Masters Students
Overheating Risk Assessment for UK schools 2023 
This project is a response to the UK’s overheating risk introduced by climate change. By 2070, climate projections for the UK estimate an increase in seasonal average temperatures of up to 5.1°C in summer as well as more intense and frequent extreme events such as heat waves.
ECCD present preliminary LATENT field trial findings 2023 
Having recently concluded the first heating season trial period for the LATENT field trial the research team have bee presenting preliminary findings at a number of events.
ECCD host Pioneering Places Workshop 2023 
ECCD host a hybrid workshop with local stakeholders about Southampton’s non-technical barriers on the pathway to net zero as part of the Pioneering Places project.
Pioneering net zero delivery for the City of Southampton 2023 
This project, currently in its second-phase will build on Southampton’s characteristics, opportunities and challenges through developing a combined techno-economic methodology coupled with stakeholder engagements to support a coherent feasibility studies to address its pathway to net zero.
ECCD Research on floating solar PV referenced by BBC Future Planet 2022 
BBC Future Planet article ‘The floating solar panels that track the Sun’ references recent 2021 ECCD paper, ‘Floating solar PV to reduce water evaporation in water stressed regions and powering water pumping: Case study Jordan’.
Sustainability Implementation Group 2022 
ECCD lead on the University Strategy-Sustainability, through the University Sustainability Implementation Group (SIG), setting the vision for a more sustainable University.
ECCD exhibit at The Big Sustainability Expo (Southampton) 2022 2022 
The Energy and Climate Change Division exhibited at The Big Sustainability Expo (Southampton) 2022 held at St Mary’s Stadium, Southampton on Thursday 22nd September.
LATENT – outreach and engagement 2022 
Article listing the range of outreach and engagement activites that have been undertaken as part of the LATENT project
ECCD undertake research for the NFRC building resilience of roofing technologies in a changing climate report 2021 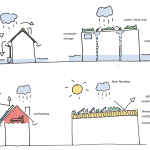
NFRC report presents research undertaken by ECCD investigating the impact that climate change will have on roofs covering the existing stock of buildings across the UK.
ECCD present at Portsmouth City Council’s BIG Climate Conversation 2021 
The Energy and Climate Change Division attended Portsmouth City Council’s Big Climate Conversation held at Portsmouth Guildhall on 9 and 10 November 2021.
ECCD research contributes to New Zealand’s Climate Change Commission consultation 2021 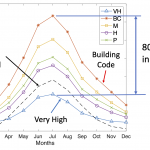
ECCD’s Dr Ben Anderson with Dr Michael Jack and Prof. Janet Stephenson from the University of Otago recently submitted a response to the New Zealand Climate Change Commission’s consultation on its first package of Advice to government. The submission focused on the results of modelling the impact of energy efficiency on space heating demand and, ...
Solar Housing KSA 2021 
The research aim is to investigate and provide evidence as to the role of solar energy systems in reducing electricity demand in residential buildings, contributing to Saudi Arabian low carbon pathway aspirations. The project will address peak demand shaving of air conditioning loads in domestic buildings and provide information to residents on energy efficiency measures.
HEART (Holistic Energy and Architectural Retrofit Toolkit) 2021 
The HEART project aims to address the increasing need for deep retrofit interventions and to develop systemic strategies leading to high performance and cost effective solutions.
APERIO: Low cost facade management in naturally ventilated buildings 2021 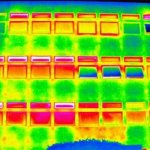
This study proposes to develop and test a low cost, non-invasive technique to assess the impact of poor facade control on energy performance and enable facilities managers to address this issue.
ECCD research highlights value of energy efficient retrofit for New Zealand’s net-zero ambitions 2020 
Dr Michael Jack and Anthony Mirfin from the University of Otago and ECCD’s Dr Ben Anderson have developed a model which suggests that building and retrofitting New Zealand’s homes to the highest currently commercial viable energy efficiency level (PassivHaus) would reduce winter heat demand by up to 80% in peak winter months. Since future space ...
De-carbonising the (English) dwelling stock – a policy tracker 2020 
UK residential dwellings are currently responsible for 15% of UK greenhouse gas emissions (or around 22% including electricity consumption) and so form a major problem for our net-zero carbon ambitions. This inconvenient but incontrovertible truth is well recognised by government in terms of increasing the energy performance (EPC Band rating) of all dwellings: “In 2017, the government ...
ECCD/SERG hosts IEA Energy in Buildings and Communities symposium and expert meeting 2020 
The Energy and Climate Change Division (ECCD) and the Sustainable Energy Research Group (SERG) within the School of Engineering at the University of Southampton, UK, hosted the IEA Energy in Buildings and Communities symposium and expert meeting
Envisioning Buildings-as-Energy-Service 2020 
The project “Developing a Tool Kit for Knowledge Integration: Envisioning Buildings-as-Energy-Service” is aimed at creating an inter-disciplinary research environment to stimulate the innovation processes related to the concept of “Buildings-as-Energy-Service”.
Thermoss monitoring strategy 2018 
Monitoring includes (a) Heat Network performance (b) indoor conditions and (c) outdoor conditions. (a) Using ultrasonic flow meters we are able to measure flows and temperatures in the heat network to monitor delivered heat and efficiency of the system without disrupting water circulation. (b) Indoor variables monitored include temperature and relative humidity in bedrooms and lounges, radiator ...
Thermoss UK heating technology demonstration sites 2018 
The Energy and Climate Change and the Sustainable Energy Research Group at the University of Southampton are directly involved in research and development of THERMOSS in the UK. This includes the deployment of heating technology packages in the residential demonstration sites (1) and (2) located in the cities of Southampton and Portsmouth. Both sites will ...
Liveable Cities – Case studies 2018 
Alongside the Little Book Series, 9 Case Studies were produced from the Liveable Cities work to showcase the breadth and applicability of the Liveable Cities research to practice and everyday life.
Liveable Cities – Little Book series 2017 
Following the roadshows and a successful closing event in the House of Lords, the Liveable Cities – Little Book series are now available online to download as PDF.
THERMOSS: Building and district thermal retrofit and management solutions 2017 
The THERMOSS project is a response to the 20% primary energy consumption reduction targets set by the 2012 European Energy Efficiency Directive (EED). This calls for effective and wide-scale building heating and cooling systems upgrade strategies. Such strategies will only be successful if they are based upon the right combination of technology innovation and ...
Energy and the City RoadShow 2017 
The Sustainable Energy Research Group is hosting a roadshow on 9th November 2017. BACKGROUND ‘Liveable Cities’ is an umbrella name for a series of interlinked research projects addressing these questions, carried out by the Universities of Southampton, UCL, Lancaster and Birmingham. Liveable Cities is hosting a series of three roadshows, one in each of its case study cities: ...
Smart Energy Research Lab 2017 
Investigators: Dr Ben Anderson, Prof Abubakr Bahaj Researchers: Dr Tom Rushby SERG is part of a team led by UCL to deliver the new GB Smart Energy Research Lab (SERL) with funding from the UK Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council. The Smart Energy Research Lab will provide a secure, consistent and trusted channel for researchers to access high-resolution ...
SERG researchers present nine papers at SET2017, Bologna, 17-20 July 2017 2017 
SERG researchers presented on a range of fields at the 16th Sustainable Energy Technologies (SET) Conference 2017, held at the Alma Mater Studiorum at the University of Bologna. Topics presented included: Wind energy: Mikey Harper and Mostafa Mahdy Thermal comfort: Rucha Amin and Victoria Aragon Urban regeneration: Philip Turner Cities and carbon-reduction potential: Luke Blunden and Massimiliano Manfren Combined heat ...
Energy Performance and Thermal Comfort in a High-Rise University Halls of Residence 2015 
This project intends to investigate the impact of occupant-related parameters on energy performance using a newly built ‘BREEAM excellent’ University Halls of residence building as a case study. More specifically, it will address the challenge of achieving energy efficiency and comfortable indoor conditions in a building which accommodates international students with potentially very different and ...
IDCOP: Innovation in design construction and operation of buildings for people 2015 
“Innovation in Design, Construction & Operation of Buildings for People” (IDCOP) is a multi institutional research programme funded under the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) Sustainable Urban Environment (SUE) programme. The aim of the IDCOP consortium is to find new ways to improve the performance of building envelopes over the whole building life ...
RENKEI Spring School – University of Southampton Southampton, UK, 22-29 March 2015 2014 
Theme: ‘District Energy Supply within Cities’ Date: 22-29 March 2015 Venue: University of Southampton Background RENKEI is the Japanese word for “collaboration” and in this context also stands for Research and Education Network for Knowledge Economy Initiatives. RENKEI is an initiative of six Japanese Universities, six UK Universities and the British Council Japan. The role of RENKEI is to offer a common ...
Liveable Cities second round of surveys online – details for participants 2014
Please follow the links below to complete your survey(s) by Monday the 17th of November if possible. Your ID number is on the e-mail and/or letter that was sent to you recently. Many thanks for your participation. If you have any questions, or if any of your contact details have changed or are incorrect, please ...
Liveable Cities 2013 
How do we address energy consumption to meet low carbon targets? How do we address infrastructure ‘lock in’ to improve the carbon performance of the urban environment? How do we engender and embed low carbon pathways and engineering solutions for demand reduction and power generation in cities? Introduction Launched in 2012, Liveable Cities is a five year £6.2m research ...
Transforming typical hourly simulation weather data files to represent urban locations 2013 
Title: Micro climate adapted localised weather data generation: Implications to the energy consumption of buildings and sustainable design of cities Researcher: Leonidas Bourikas Supervisors: Patrick A.B. James & AbuBakr S. Bahaj Abstract This thesis has investigated methodologies for the adaptation of airport based simulation weather files to replicate the local micro climate. The objective of this thesis is to propose a simple method for the generation ...
‘Why waste heat?’ 2009 
ECCD was commissioned by the Institute of Civil Engineers to generate a report on the potential of heat recovery from centralised electricity generation in the UK.
Climate change building impact assessment studies 2009 
Climate change is one of the largest threats both for the global economy and the local community. It is predicted that, by 2100, average temperatures could rise as much as six degrees Celsius. The UK is anticipated to become hotter and drier in summer and milder and wetter in winter even under low carbon emissions ...
Environmental Building Monitoring 2007 
Several University of Southampton case study buildings of different age and state of repair have been monitored over longer time periods looking at environmental parameters such as temperature, relative humidity and carbon dioxide concentration. Measurements were made at five minute intervals over several weeks for each building. The scope of these studies was to identify ...
Photovoltaics in Residential Applications 2007 
Residential grid connected PV systems are relatively simple to design with easy to predict annual yields. However, the headline economics of residential PV in the UK are at present unattractive. A typical small residential PV system (1 to 3 kWp) as shown in the top figure would cost in the year 2000 around £4,500 per ...
Deterioration of Environmental Conditions 2006 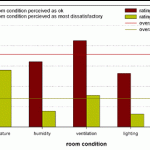
Further occupant surveys conducted by the group have shown that compromising one aspect of the indoor comfort conditions can lead to a perceived compromising of all other measures of indoor comfort. A survey conducted in June 2005 inside existing offices adjacent to the PV atrium (c in Figure 1) reveiled a significantly worse perception of indoor ...
In industrialised countries building refurbishment is generally considered to be vital in order to achieve major carbon emission reductions in the built environment. At high latitudes the largest single consumer of energy in buildings continues to be space heating required for creating comfortable indoor conditions. For example, a typical 3 bedroom UK house has, on ...
Ventilation Behaviour in Relation to Carbon Dioxide Concentration and Air Temperature 2006 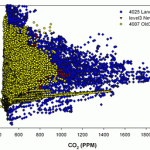
The carbon dioxide concentration levels normally observed in indoor environments range from 350 to 2,500 ppm and are typically between 500 and 1,500 ppm. Current literature suggests that a building’s carbon dioxide concentration can be seen as an indicator for both volatile organic component (VOC) concentration and general indoor air quality. However, the potential to ...
What is Good Building Performance? 2006 
The question of how to qualify and quantify good building performance is not trivial to answer. A well performing building from a carbon footprint perspective may not automatically be well performing in terms of occupant satisfaction (Figure 1). Similarly building performance may be understood quite differently by different groups of building users as ‘performance’ can be ...
Environmental Control Facilities and User Interaction 2006 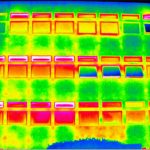
The group’s research has highlighted that at present environmental control facilities are often not correctly applied, or more usually, incorrectly used due to their complexity or unintuitive mode of operation. It has been shown that there is often lack of interaction between users and their buildings. Façade interaction studies of an office building highlighted rather low ...
B-space: Building Specific Pre-refurbishment Assessment of Comfort and Energy 2006 
Within the framework of the IDCOP research project a pre-refurbishment tool for assessing buildings was developed (Figure 1). This tool which is termed B-space assesses the energy demand of multi-storey office buildings taking into account occupier comfort. B-space is targeted at asset mangers as main user group. It enables calculation of a building’s carbon footprint and ...
Climate Change Implications for the Urban Environment 2005 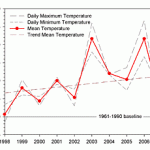
Human-made emissions be it from buildings, business, agriculture or transport are now commonly accepted to be the main cause of the global warming trend which is currently being experienced. The Sustainable Energy Research Group is conducting research on climate change issues by assessing future climate impacts in particular in terms of the future performance of buildings. ...
Solar PV Systems at Highfield Campus, Southampton 2005 
The University of Southampton has three permanently grid connected PV systems on its Highfield Campus designed and serviced by the Sustainable Energy Research Group. The installed capacity of these three facilities is about 20 kWp: (a) George Thomas Building – 12.2 kWp atrium (b) Building 2 – 7.2 kWp vertical façade (c) Eustice Building – 0.4 kWp roof ...
Assessment of Urban Microgeneration Solutions 2004 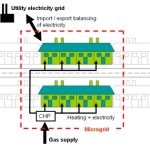
The group’s research is looking at existing housing developments from the 1970s, 1980s, 1990s and 2000s to determine the scope and potential impact of microgeneration technologies and energy efficiency measures on the residential scale.
Holographical Optical Elements (HOE) for high efficient illumination, Solar Control and Photovoltaic Power in Buildings 2001 
The Sustainable Energy Research Group has been involved in an EU FP5 research project on High Efficiency HOEs investigating HOEs for building applications as well as testing their compliance as a building material. Within this project the work of the researchers in Southampton centred on HOEs as a solar shading solution. Bespoke thermal simulation models ...

