
Energy and Climate Change Division (ECCD) undertake research to support the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia’s (KSA’s) Vision 2030. The research is in collaboration with the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, King Abdulaziz University (KAU), supported by King Salam Bin Abdulaziz Chair in Energy Researcg and KSA Ministry of Education.

Heat networks provide a high efficiency, low cost option for energy supply based on combined heat and power concepts. Analysis of heat networks performance and deployment of smart heating technologies are mainly applied in heat networks in social housing settings within the cities of Southampton and Portsmouth.

REPLENISH contends that if our infrastructure systems and their associated cityscapes were designed with positive health and wellbeing outcomes as the primary design criterion, huge social and economic benefits would result. REPLENISH therefore proposes, by adopting systems thinking and systems engineering (or ‘doing’), to rethink and redesign our engineered infrastructure systems and cityscapes.
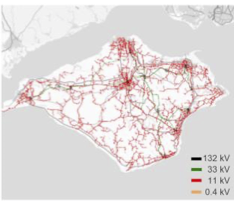
In the UK, the Isle of Wight (IoW) wish to become self-sufficient in electricity from renewable sources, which is likely to be achieved through the deployment of utility-scale solar PV farms augmented with rooftop solar PV systems.
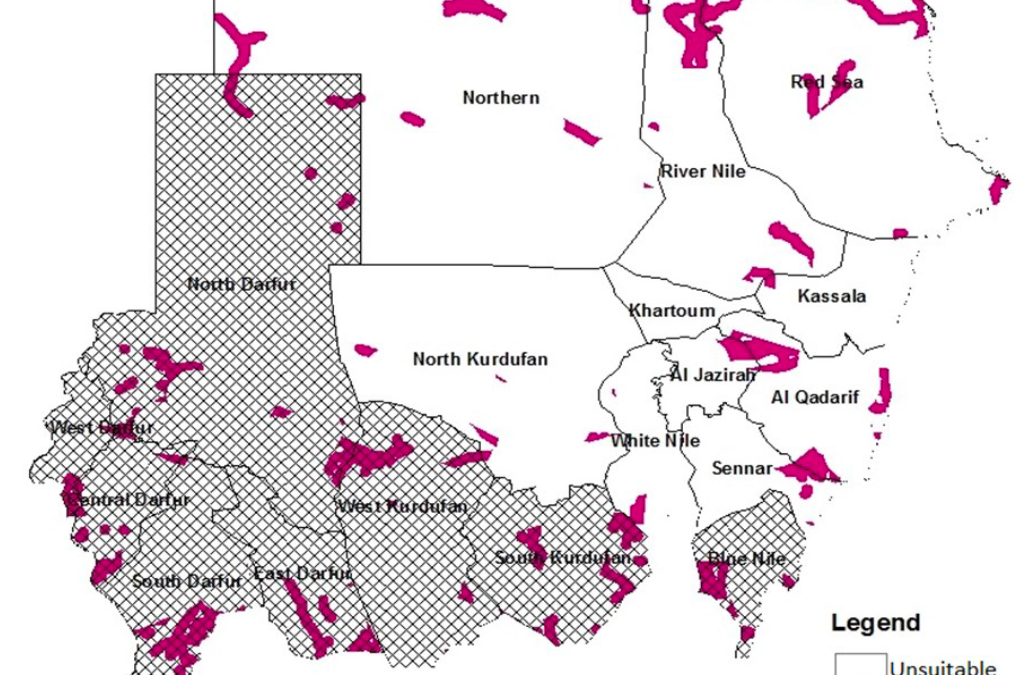
This research aims to investigate the potential for implementing clean off-grid energy systems for rural electrification in Sudan. Analysis using the GIS (Geographic Information System) -MADM (Multiple Attribute Decision Making) method will identify sites suitability for renewable off-grid electricity systems. The methodology includes four main strands of work: (a) assessment of renewable energy availability in Sudan, (b) identifying suitable weighting criteria for site selection, (c) location of appropriate sites that fulfil the criteria via MADM-GIS, and (d) performing experts’ NGT (Nominal Group Technique) via AHP (analytic hierarchy process) – SAW (simple additive weighting) to select the most suitable sites in rural Sudan.
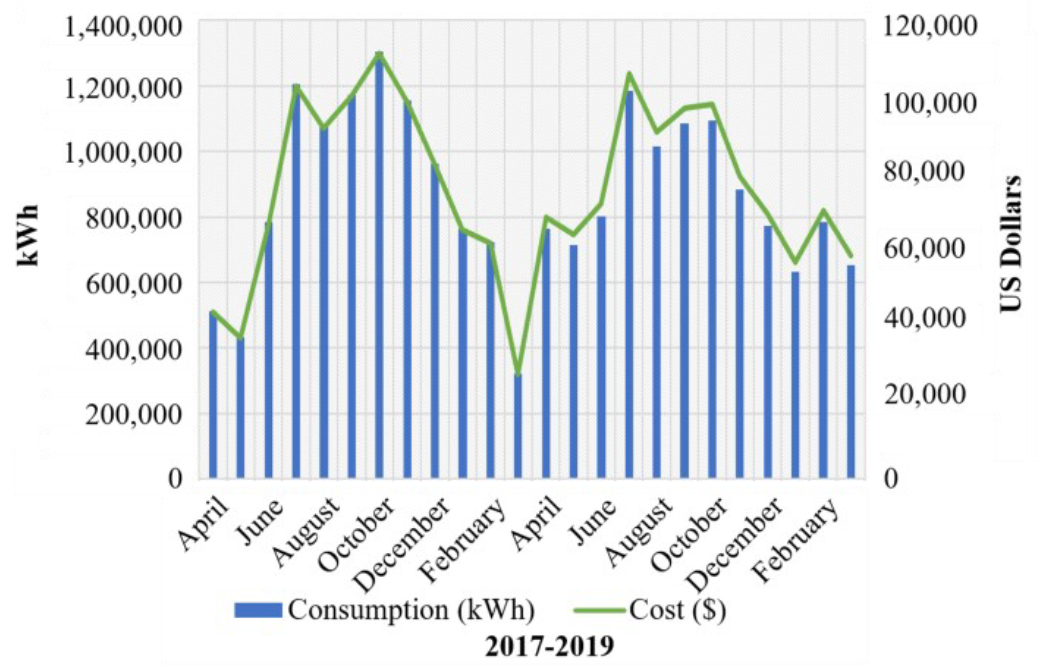
This research studies the impact of PV penetration on the grid of the University of Jeddah Campus, knowledge generated will support analysis on a medium size city in KSA to displace fossil fuel power supply currently been used.






